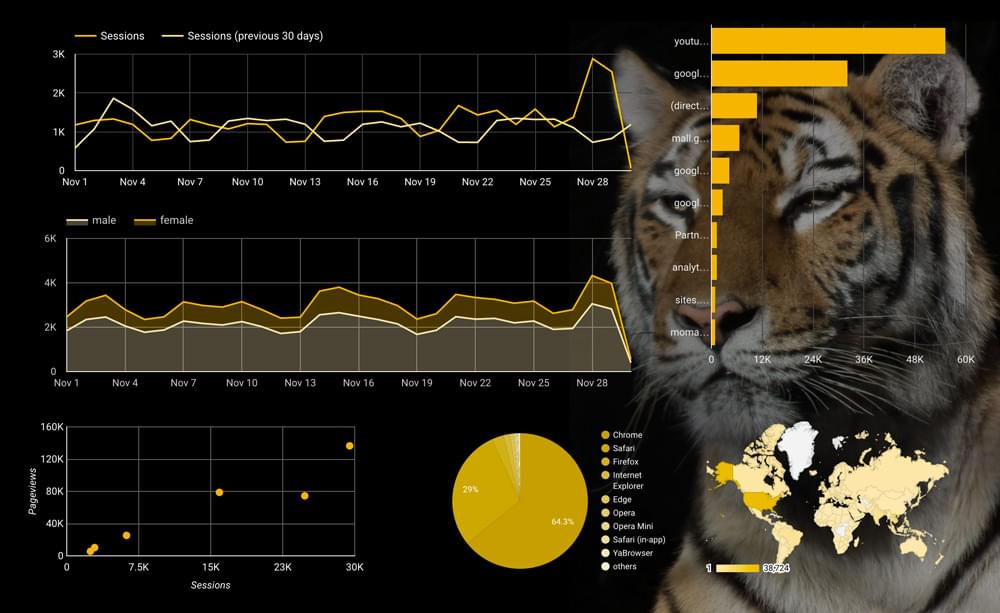
Google Data Studio: a Nifty, Free, Easy-to-use Data Vis Tool
As a digital marketer, you can often be overwhelmed with the amount of information and data needed to be analyzed in order to evaluate your efforts. Traffic, conversion rate, user location, behavior and acquisitions — just to name a few — all have to be examined to define the progress of your digital marketing campaign.
Client reporting is one of the biggest challenges digital marketers face when undertaking projects. Although endless numbers and stats may make some sense to internet professionals, generally customers are not as tech savvy.
Anyone can export masses of information from Google Analytics to an excel spreadsheet, but how do you present the data in a way that’s easy to digest? The answer is — Data Visualization.
What is Data Visualization?
Data Visualization is a way of representing complex data and stats in a pleasing, visually-appealing way. Visual data may include components like pie and graph charts, maps or tables, and can be presented in different forms, such as infographics, videos, illustrations and interactive reports.
Why is it important? The answer is simple. Our brains absorb visual information better, faster, more easily.
Benefits of Data Visualization
The benefits of visualizing data include:
- providing clearer information for clients
- making it easier to view and analyze patterns and trends
- enabling interaction with the data
- allowing for more information to be absorbed, and more quickly
- better identify peaks and troughs.
In this post, we’re going to assess how a new tool, Google Data Studio, can help us build beautiful and interactive reports.
Google Data Studio
Google Data Studio (GDS) is a new tool by Google that makes it easy to create beautiful, engaging, responsive, branded and interactive reports. It does this by pulling metrics from Google’s properties, such as Google Analytics, Adwords and YouTube Analytics, as well as spreadsheets and SQL databases.
For this article, we’ll be using Data Studio to create a visual report using Google Analytics data. To do this, you first need to have an active Google Analytics property that is properly integrated with the website.
The same applies to other reports. If you wish to pull the data from your Adwords or YouTube Analytics, make sure to sign in with an appropriate Google account that has that data.
Getting started
The following 18 steps will walk you through the process of creating a visual report from your Google Analytics data.
Step 1
Go to Google Data Studio and log in with your Google Analytics credentials:
Step 2
As soon as you log in, you’ll be presented with the following dashboard:
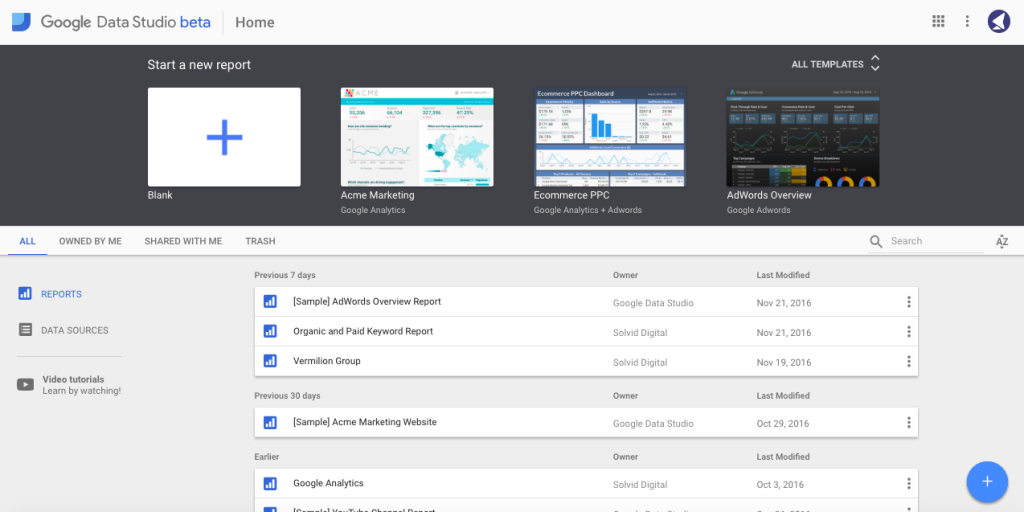
This page is a primary control panel for your GDS projects. Here you can choose a pre-designed template, create new reports from scratch, add new data sources, manage your existing projects and watch video tutorials.
One thing to note here is that, with the free version, you can only add up to 5 custom reports.
Step 3
All reports start with adding a data source. In other words, providing GDS with access to the information that’s intended to be used in the report.
Let’s go ahead and add a new Google Analytics data source by clicking on a Data Sources button in the left hand side of the dashboard:
Step 4
You’ll then be directed to the screen with the list of already connected data sources. To add a new one, click on the blue “Add” (+) button.
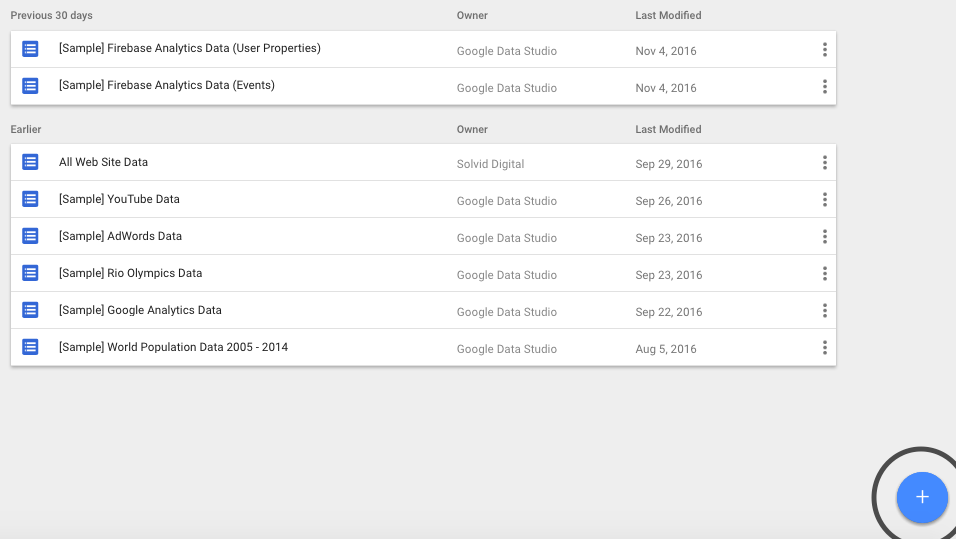
Step 5
On the next page, add a unique name to your new project, select “Google Analytics” from the list of connectors, choose the relevant account, property, and hit the Connect button in the right-hand corner of the screen:
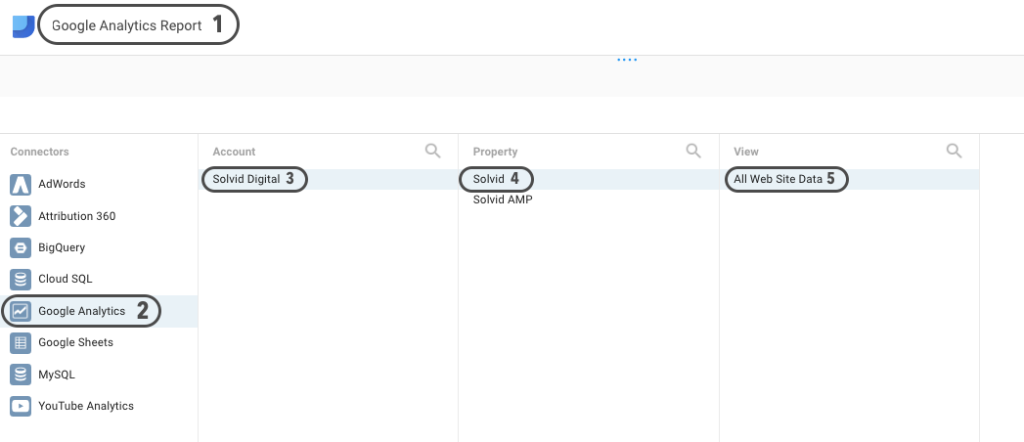
Step 6
Next, you’ll be bombarded with the following screen, which, at first, may seem quite challenging to digest. However, it’s not as horrifying as it looks.
In simple terms, this is just a list of metrics and dimensions available to be used in the report. Each field is assigned a unique type: Numeric, Text, Date & Time, Boolean, Geo or Currency. When pulling data from Google’s properties (such as Google Analytics or Adwords) GDS will assign the value automatically. However, if you’re using custom data pulled from an Excel Document, you’ll have to ensure that every field is assigned an appropriate type.
In this instance, you wouldn’t need to change any fields, so it’s safe to go ahead and click Create Report in the right-hand corner of the screen.
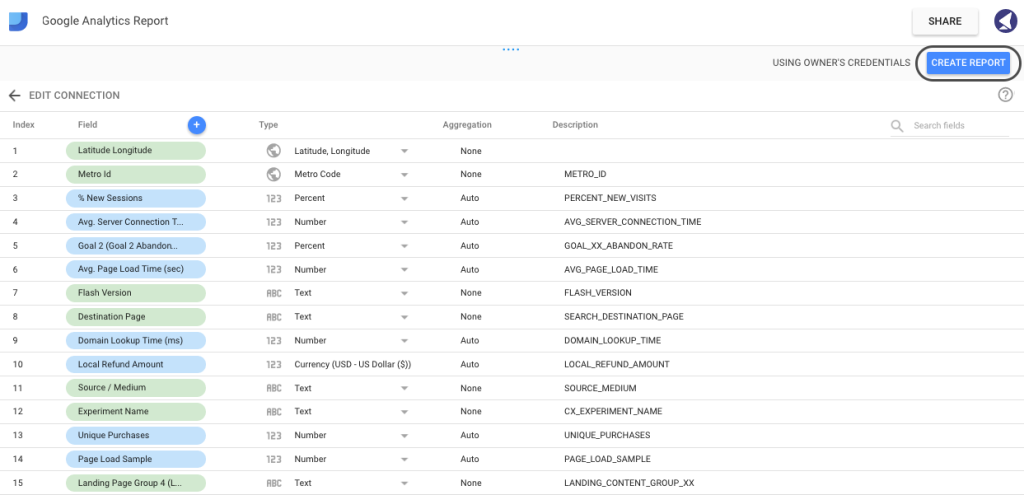
Step 7
Next, you’ll be redirected to the screen with the actual design canvas. Give a name to your report and select the data source we’ve just created:
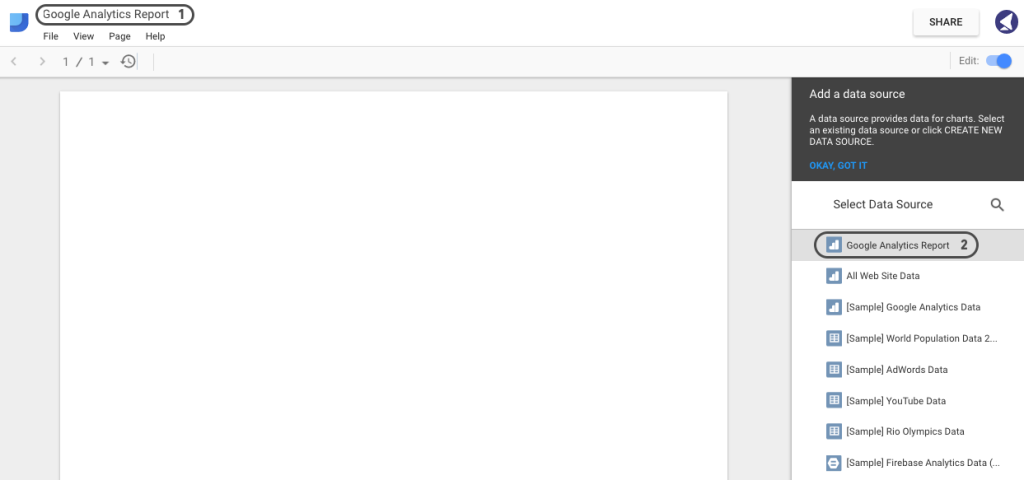
Step 8
As soon as you connect the data source with the report, you’ll notice a control panel at the top of the canvas.
Currently, you can add the following components to your report: time series, bar chart, pie chart, table, geo map, scorecard, scatter chart, bullet chart, area chart, text, image, rectangle, circle, date range and filter control.
Step 9
You can also change the orientation of the page to landscape. To do this, go to File > Report and theme Settings > Layout > Landscape:
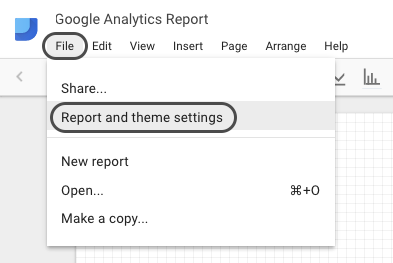
However, in this guide, we’ll be using portrait orientation.
Step 10
Now that we have our canvas ready, let’s proceed with adding some branding and custom styling.
Chances are, you’re creating these reports for clients. Hence, custom branding is an essential part of making your reports visually appealing.
Let’s add a header by using the rectangle tool. Select the area where you want your shape to appear.
In the right sidebar, you’ll see some styling options, allowing you to choose the color, border radius, opacity, border size and color:
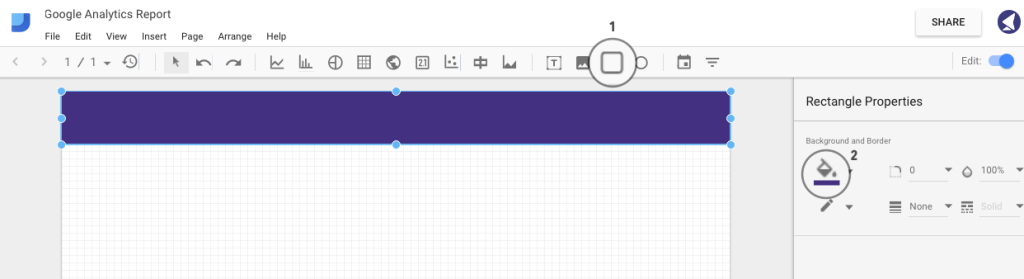
Step 11
Let’s go ahead and add a logo to our report. Click on the image tab as shown below and select the area where you want your logo to appear. Then, hit the Data tab in the right sidebar and select an image file.
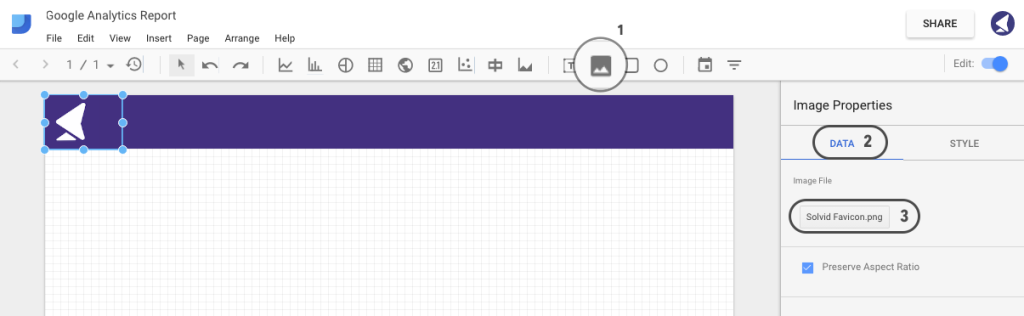
Step 12
What’s fascinating about Google Data Studio is that it allows adding an interactive date range, which will automatically change the graph data according to the date range.
To add one, click on the Date Range tab and select the area where you want the handle to appear. Then, choose your default date range and tailor the styling:
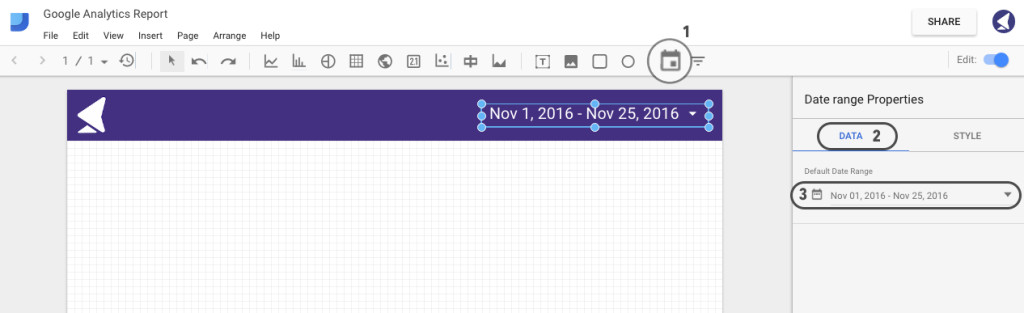
Step 13
Once we have the basics ready, we can proceed with further styling and adding the actual data to our report. Let’s start off with some general score cards.
A score card is simply a single metric that can be used to represent some general information, such as total visitors, total sessions, bounce rate, etc.
We’ll now proceed with adding four score cards, representing sessions, pageviews, users and bounce rate.
First, go ahead and add a score card using the tab as shown on the image below.
Then, in the right sidebar, select the preferred metric to be used for this particular score card. For our first example, we’ve chosen to display sessions:
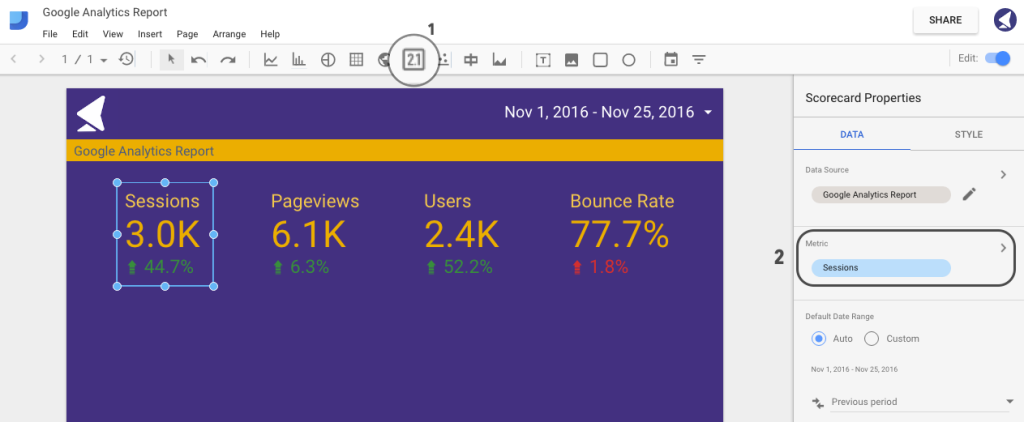
You can then copy and paste this score card, changing the metric source.
Step 14
It’s now time to add a first graph that will represent a number of sessions and pageviews for our selected date range.
First, hit on the Time Series tab and select the area where you want your graph to appear. Then, select the metric sources. In this case, we’ll be using sessions and pageviews:
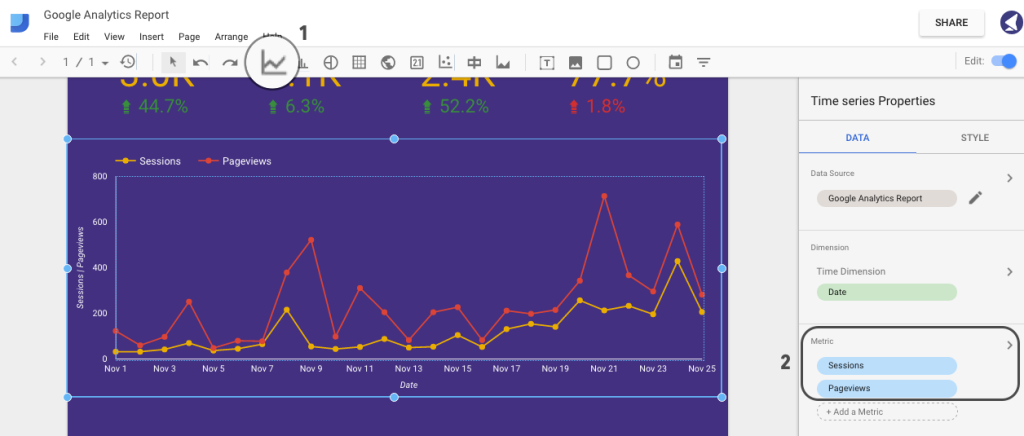
Step 15
Let’s now add a bar chart representing session sources.
Click on the Bar Chart and select the area where you want it to appear. Then, select Source in Data > Dimensions:
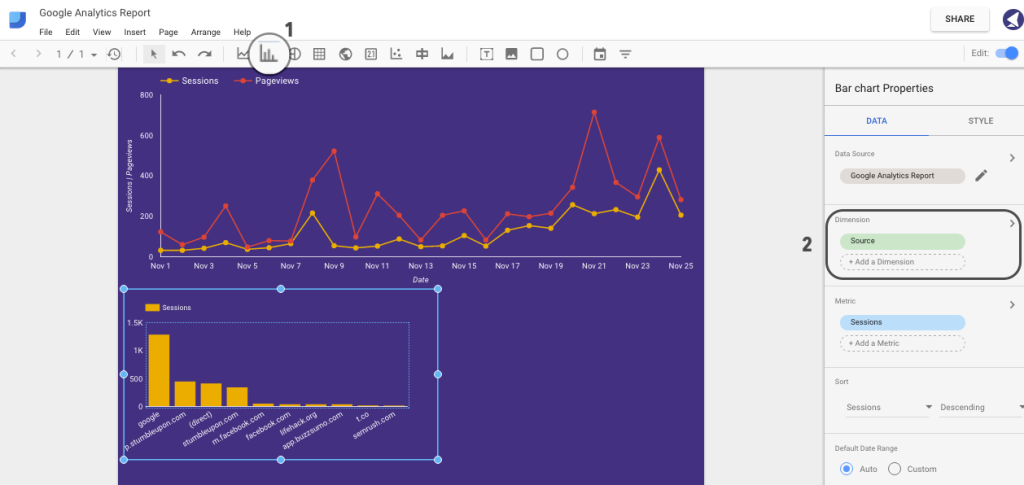
Step 16
We can now add a pie chart representing a breakdown of sessions by devices (that is, desktop, mobile and tablet).
To do that, hit the Pie Chart tab and select Device Category under Dimension section in the right sidebar:
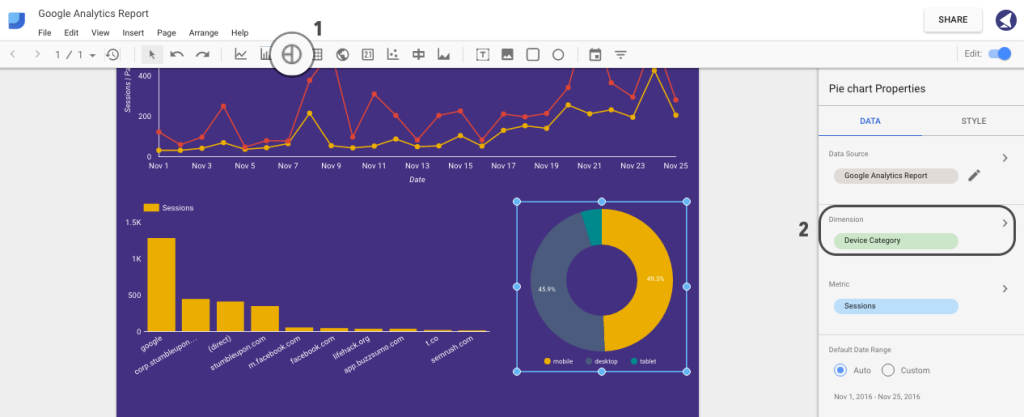
Step 17
Last but not least, let’s add a geographical map and table of users. Click on Geo Map, select Country ISO Code from the dimensions list, and select users from a list of metrics.
To add a table of top countries by users, click on the Table tab and choose the same metrics as for Geo Map:
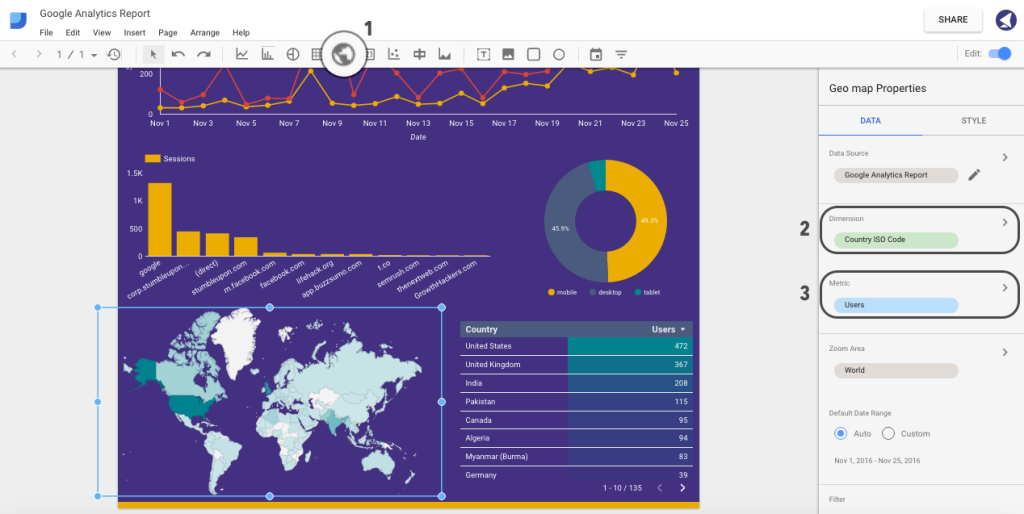
That’s it. Here is how our final version looks:
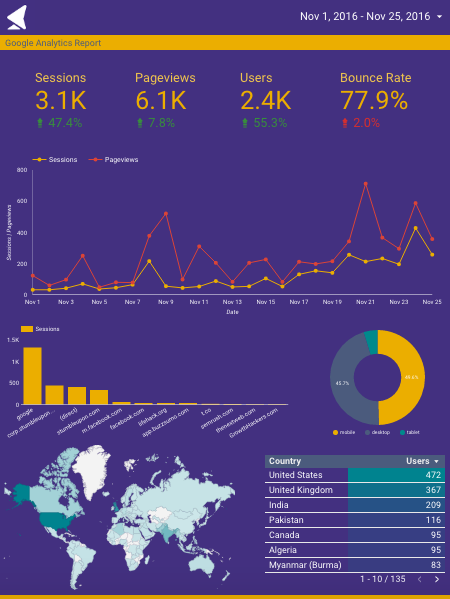
Step 18
Now that we have everything ready, it’s time to go ahead and share this report with our colleagues or clients.
Tap the Share button in the top-right corner of the screen.
You can either copy the shareable link or enter email addresses of people you want to send this report to:
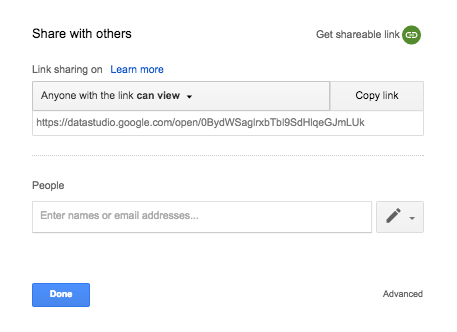
To Conclude
Hopefully, after reading this guide, you now have an idea of how important and powerful data visualization can be, and how to incorporate Google Data Studio to provide your clients with comprehensive, easy-to-understand interactive reports.
We’d love to hear your thoughts and any experiences you’ve had with this tool.