6 Tools for Debugging React Native
Debugging is an essential part of software development. It’s through debugging that we know what’s wrong and what’s right, what works and what doesn’t. Debugging provides the opportunity to assess our code and fix problems before they’re pushed to production.
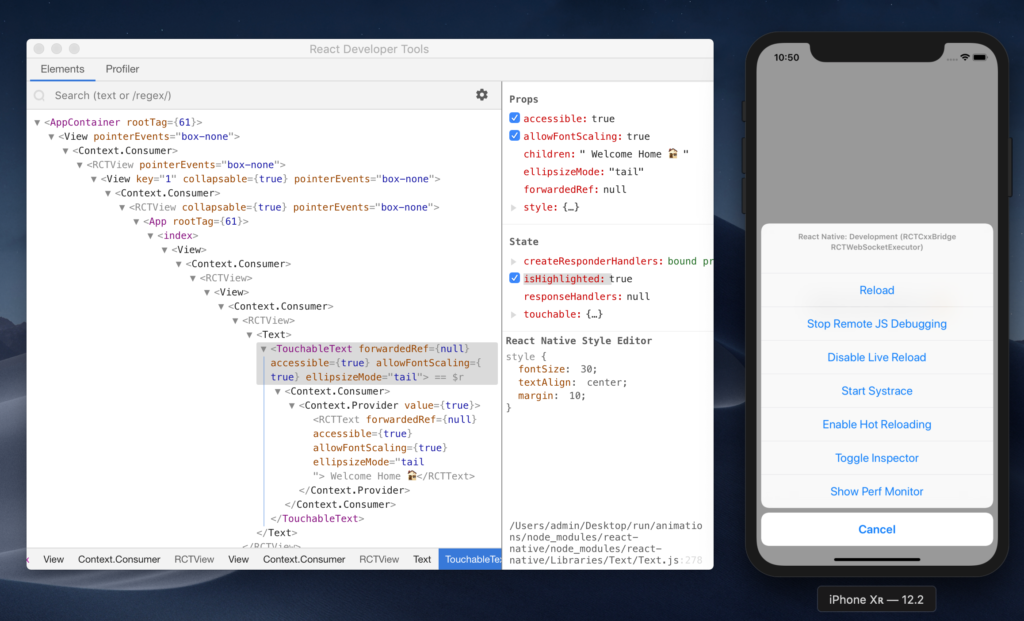
In the React Native world, debugging may be done in different ways and with different tools, since React Native is composed of different environments (iOS and Android), which means there’s an assortment of problems and a variety of tools needed for debugging.
Thanks to the large number of contributors to the React Native ecosystem, many debugging tools are available. In this brief guide, we’ll explore the most commonly used of them, starting with the Developer Menu.
Debugging is twice as hard as writing the code in the first place. Therefore, if you write the code as cleverly as possible, you are, by definition, not smart enough to debug it. — Brian W. Kernighan
The Developer Menu
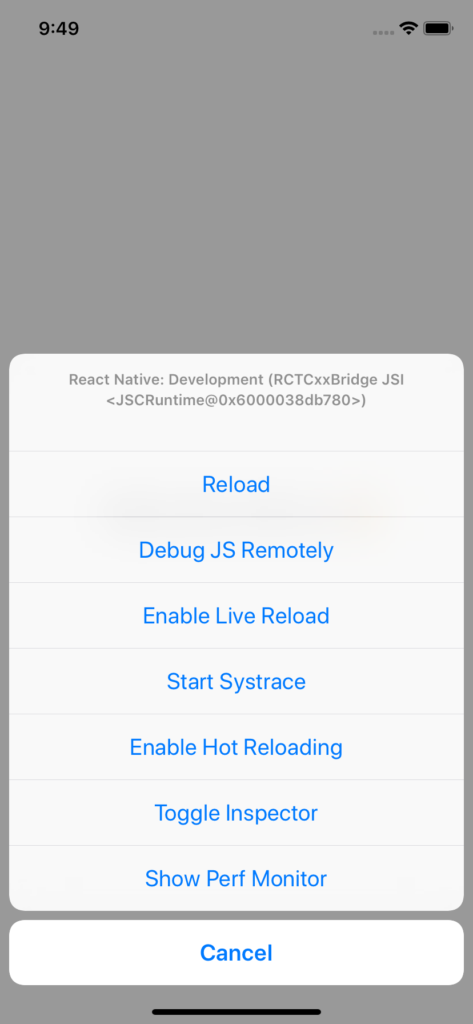
The in-app developer menu is your first gate for debugging React Native, it has many options which we can use to do different things. Let’s break down each option.
- Reload: reloads the app
- Debug JS Remotely: opens a channel to a JavaScript debugger
- Enable Live Reload: makes the app reload automatically on clicking Save
- Enable Hot Reloading: watches for changes accrued in a changed file
- Toggle Inspector: toggles an inspector interface, which allows us to inspect any UI element on the screen and its properties, and presents and interface that has other tabs like networking, which shows us the HTTP calls, and a tab for performance.
YellowBoxes and RedBoxes
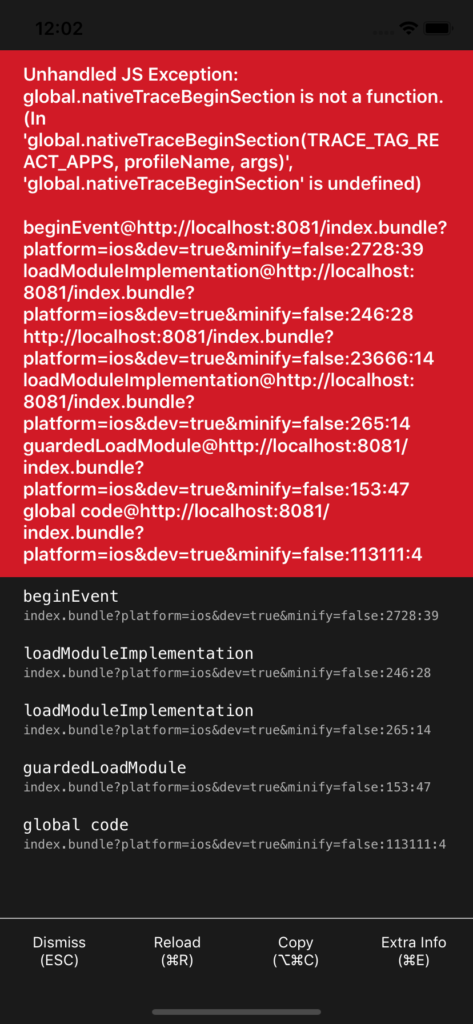
RedBoxes are used to display errors. Every time an app throws an error, it will display a RedBox and the description of the error. You can display it any time by writing console.error. But it doesn’t work in the production, meaning that if an error happens in that environment, the app will crash and stop running.
The RedBox is your friend. One of the helpful things about it is that it displays the error and gives you the suggestions on how to fix it, which you won’t find in the console. For example, I’ll frequently write a style property that’s not supported by React Native, or a property that’s used for a specific element—such as setting backroundImage for the View element. The Redbox will throw an error, but it will also show the list of supported style properties that you can apply to the View.
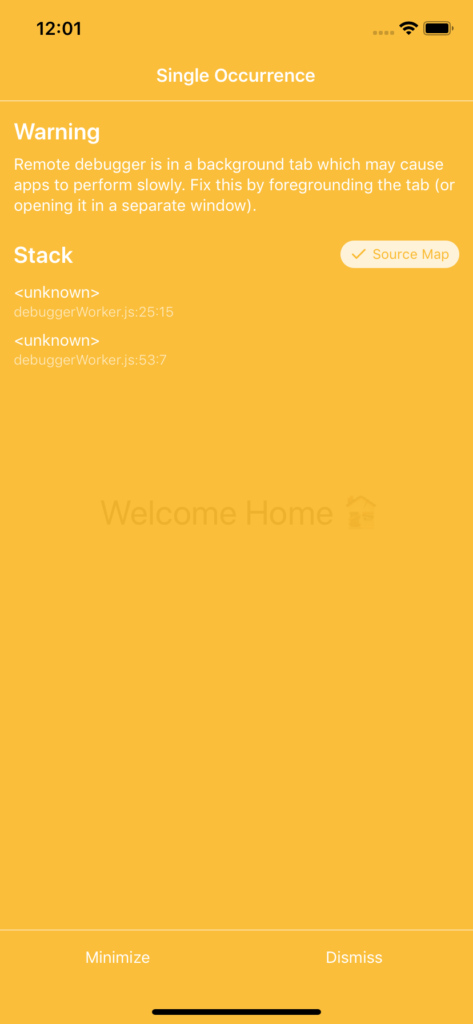
YellowBoxes are used to display warnings. You can disable them by adding line of code shown below inside index.js in the root directory of your app. But that’s not recommended, as YellowBoxes are very useful. They warn you about things like performance issues and deprecated code. You can use the YellowBox element from react-native to display a specific warning.
import {YellowBox} from 'react-native';
YellowBox.ignoreWarnings(['Warning: ...']);
Most YellowBox warnings are related to some bad practice in your code. For example, you might get a warning that you have an eventListener that you aren’t removing when the component unmounts, or that you have deprecated features and dependencies like this:
warning: ViewPagerAndroid has been extracted from react-native core and will be removed in a future release. It can now be installed and imported from '@react-native-community/viewpager' instead of 'react-native'. See https://github.com/react-native-community/react-native-viewpager
Fixing these issues will prevent many bugs and will improve the quality of your code.
You can always learn more about debugging React Native in the official docs.
Chrome’s DevTools
Chrome is possibly the first tool you’d think of for debugging React Native. It’s common to use Chrome’s DevTools to debug web apps, but we can also use them to debug React Native since it’s powered by JavaScript.
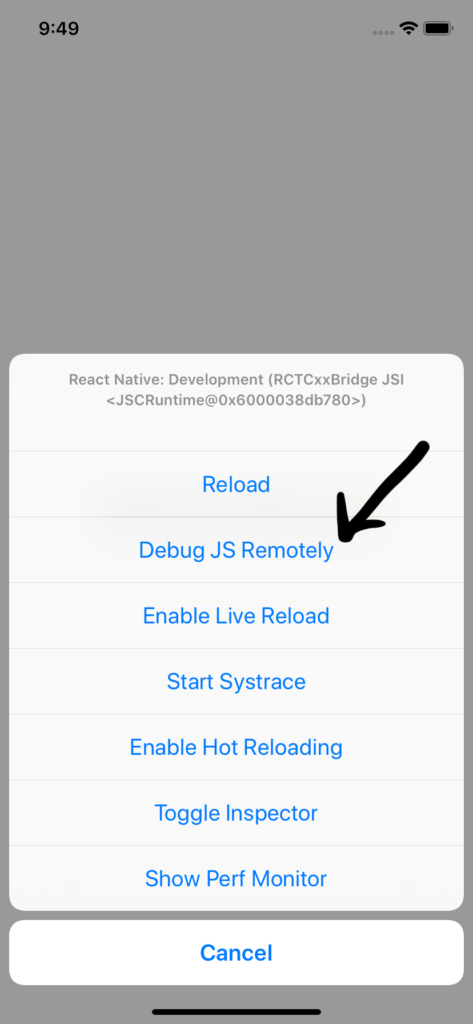
To use Chrome’s DevTools with React Native, first make sure you’re connected to the same Wi-Fi, then press command + R if you’re using macOS, or Ctrl + M on Windows/Linux. When the developer menu appears, choose Debug Js Remotely. This will open the default JS debugger.
Then check this address http://localhost:8081/debugger-ui/ in Chrome. You should see this page:

You may have to do some troubleshooting on Android.
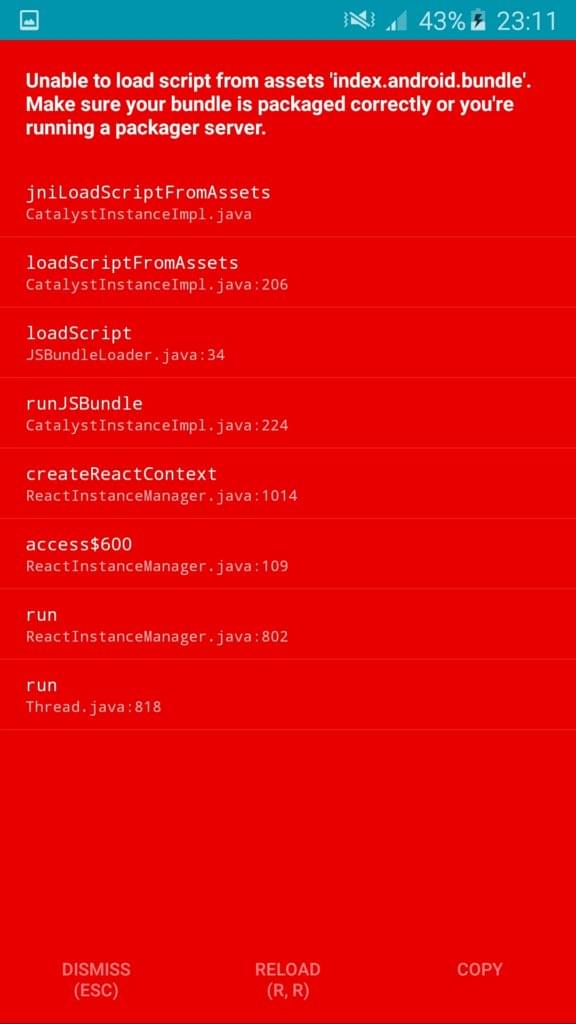
To solve this problem, make sure your your machine and the device are connected on the same Wi-Fi, and then add android:usesCleartextTraffic="true" to android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml. If this doesn’t work for you, check out these links for other solutions:
After you have successfully connected to Chrome, you can simply toggle the Chrome inspector.
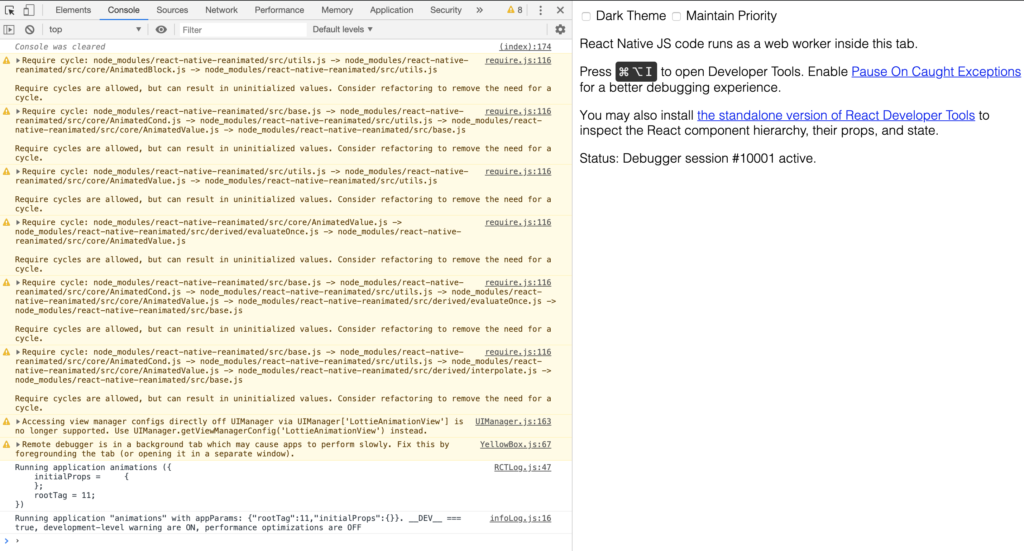
Then take a look at the logs of your React Native app. Also have a look through the other features offered by Chrome’s DevTools, and use them with React Native as you do with any Web app.
One of the limitations of using Chrome’s DevTools with React Native is that you can’t debug the styles and edit the style properties as you usually do when you debug web apps. It’s also limited in comparison with React’s devtools when inspecting React’s component hierarchy.
React Developer Tools
To debug React Native using React’s Developer Tools, you need to use the desktop app. You can install it globally or locally in your project by just running this following command:
yarn add react-devtools
Or npm:
npm install react-devtools --save
Then start the app by running yarn react-devtools, which will launch the app.
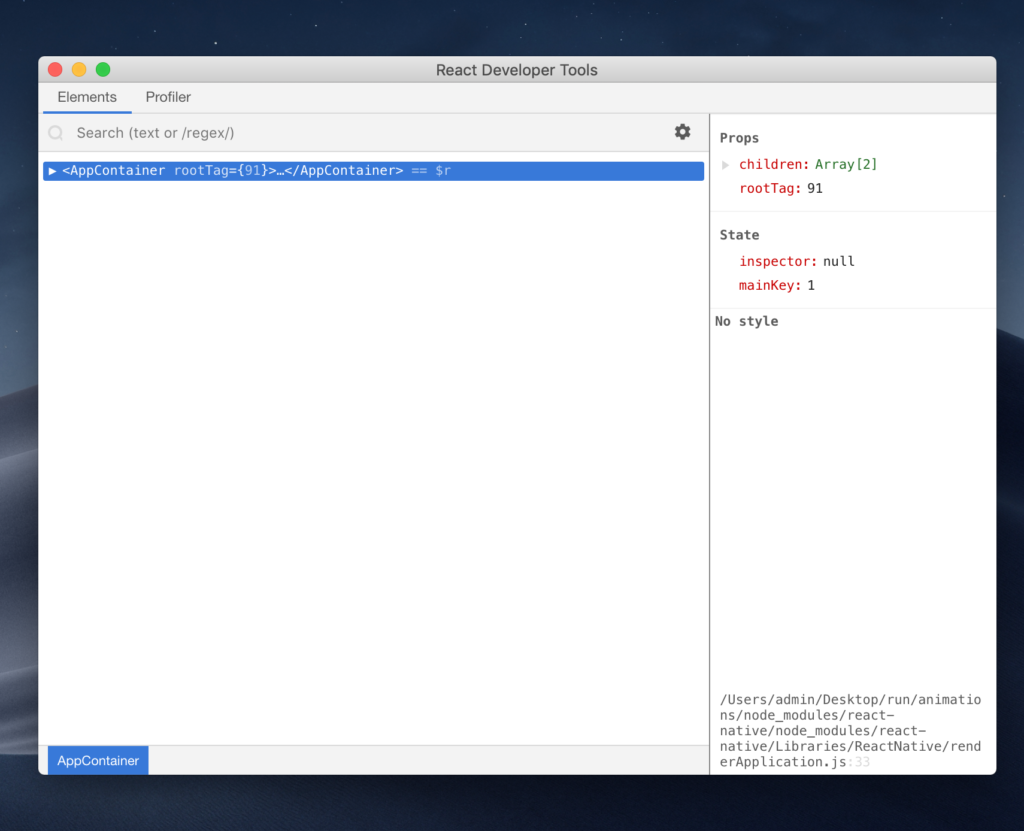
React’s Developer Tools may be the best tool for debugging React Native for these two reasons:
- It allows for debugging React components.
- It makes it possible to debug styles in React Native (my favorite feature of these developer tools!). The new version comes with this feature that also works with inspector in the developer menu. Previously, it was a problem to write styles and have to wait for the app to reload to see the changes. Now we can debug and implement style properties and see the effect of the change instantly without reloading the app.
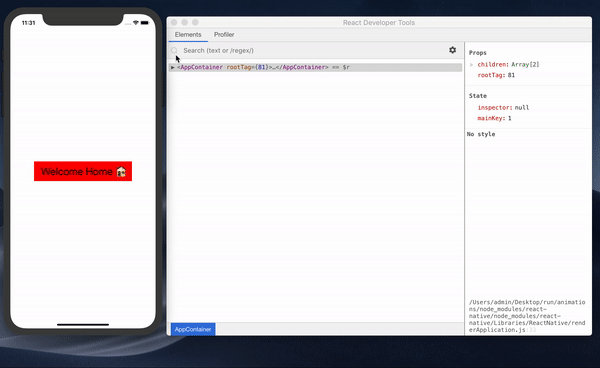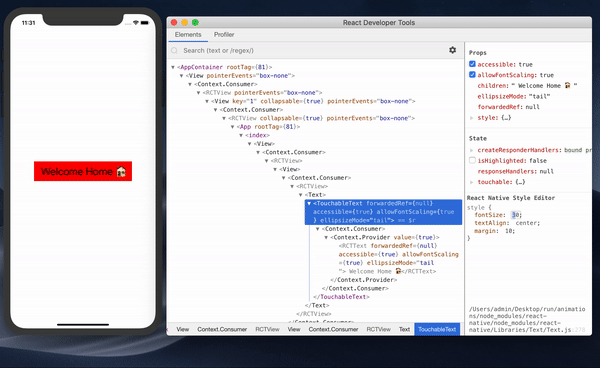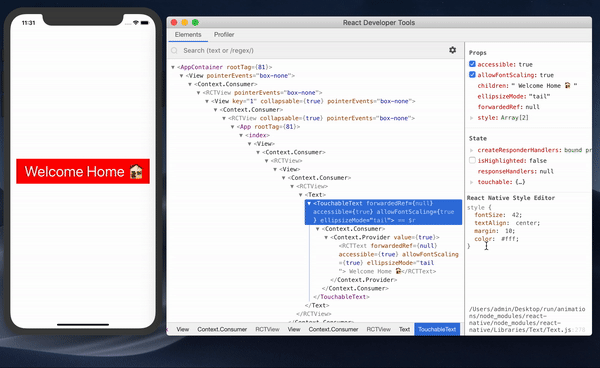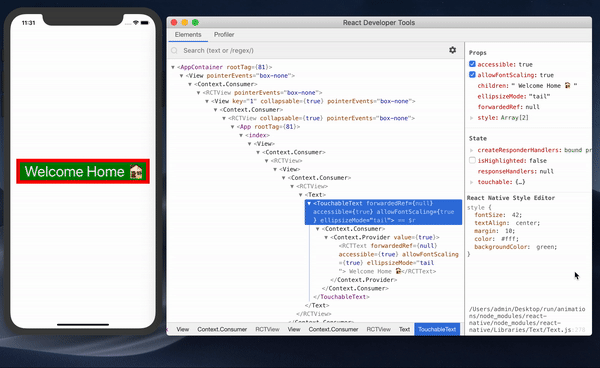
You can learn more about using React’s Developer Tools app here.
React Native Debugger
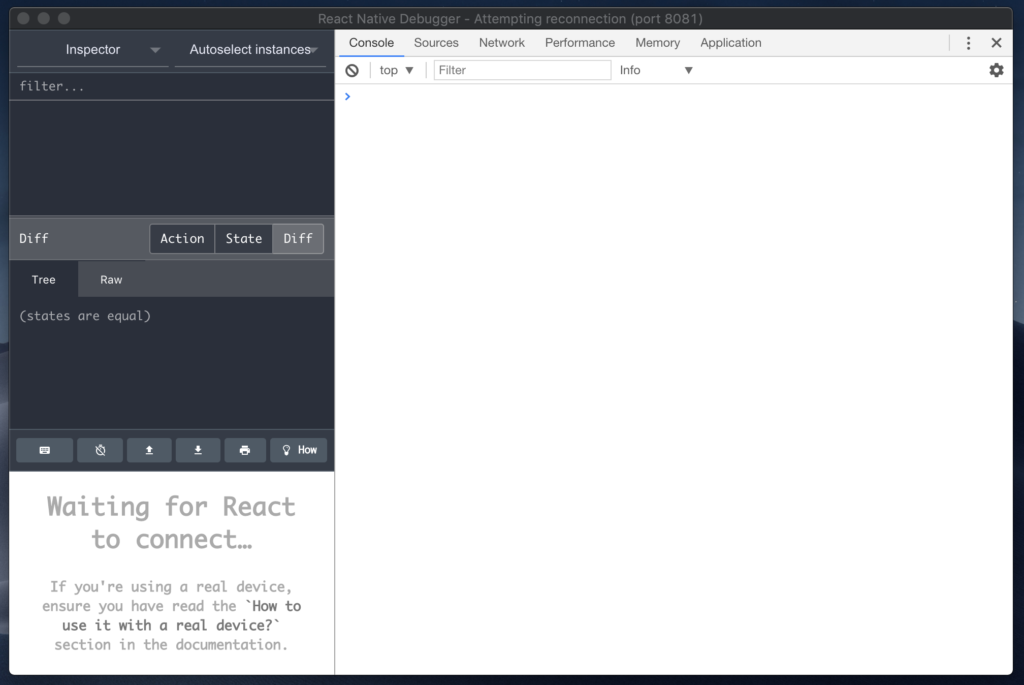
If you’re using Redux in your React Native app, React Native Debugger is probably the right debugger for you. It’s a standalone desktop app that works on macOS, Windows, and Linux. It integrates both Redux’s DevTools and React’s Developer Tools in one app so you don’t have to work with two separate apps for debugging.
React Native Debugger is my favorite debugger and the one I usually use in my work with React Native. It has an interface for Redux’s DevTools where you can see the Redux logs and the actions, and an interface for React’s Developer Tools where you can inspect and debug React elements. You can find the installation instructions here. You can connect with this debugger in the same way you open Chrome’s inspector.
Using React Native Debugger over Chrome’s DevTools has some advantages. For example, you can toggle the inspector from the Dev Menu to inspect React Native elements and edit styles, which isn’t available in Chrome’s DevTools.
React Native CLI
You can use the React Native CLI to do some debugging as well. You can use it for showing the logs of the app. Hitting react-native log-android will show you the logs of db logcat on Android, and to view the logs in iOS you can run react-native log-ios, and with console.log you can dispatch logs to the terminal:
console.log("some error🛑")
You should then see the logs in the terminal.

You can use the React Native CLI to get some relevant info about the libraries and the dependencies you’re using in your app, by running react-native info on the terminal. It shows us some useful info about the tools you’re using. For instance, here’s an example of an output when you run react-native info:
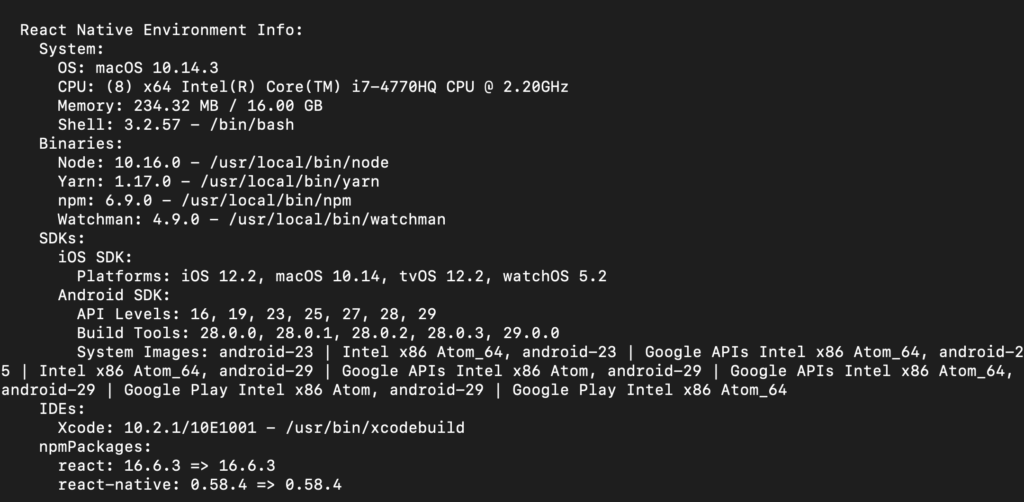
You can use this info to fix some bugs caused by version mismatches of a tool you’re using in your project, so it’s always good to check the environment info using this command.
Summary
There are lots of tools for debugging React Native in addition to the ones we’ve looked at here. It really depends on the specific needs of your project. I mostly use React Native Debugger Desktop because I often work with Redux, and it combines an array of tools in one app which is great and a time saving.
Please hit me on Twitter if you’d like to talk more about tools to debug React Native and about React Native in general. I’d love to hear from you!
